Items
Auditory Nerve Test System During Vestibular Schwannoma Resection
Brief Summary:
The Auditory Nerve Test System (ANTS) is a novel device that stimulates the auditory nerve much like a cochlear implant. The purpose of this study is to demonstrate feasibility of the ANTS during translabyrinthine surgery for vestibular schwannoma resection. If the auditory nerve is kept intact, then the patients will also receive a cochlear implant at the same time potentially alleviating the morbidities caused by a vestibular schwannoma and asymmetric sensorineural hearing loss.
Learn more on clinicaltrials.gov »
Contact Dr. Cameron Wick, cameron.wick@wustl.edu.
Cisplatin, Nab-Paclitaxel, and Cetuximab (CACTUX) in Patients With Incurable Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (CACTUX)
Brief Summary:
The purpose of this research study is to look at the effect of a treatment regimen called CACTUX on head and neck cancer. The CACTUX regimen is a combination of three drugs called cisplatin, nab-paclitaxel, and cetuximab (although carboplatin may be given in place of cisplatin if participants have previously had problems receiving cisplatin). The use of nab-paclitaxel in this combination is different from routine care, in which a drug called 5FU is often given instead, but the investigators group has conducted previous research where the investigators incorporated nab-paclitaxel into routine treatment with cisplatin, 5FU, and cetuximab. The investigators are looking at the incidence of side effects with the CACTUX regimen as well as response of the disease and health status.
For more information , contact: Douglas R. Adkins, MD, 314-362-5654, dadkins@wustl.edu
Cochlear Implantation in Adults With Asymmetric Hearing Loss Clinical Trial
Brief Summary:
This longitudinal study evaluates the possible benefit of cochlear implantation in the poor ear of adults with asymmetric hearing loss who continue to use a hearing aid in the better hearing ear.
For more information, contact: Noel Dwyer, AuD (dwyern@wustl.edu) or Laura Holden, AuD (laurakholden@wustl.edu), or 800-437-5930
Davidson Lab
The primary focus of my research is to examine the perceptual, cognitive, and audiological factors influencing speech and language outcomes in children with cochlear implants (CIs) and hearing aids (HAs). The foundation for this multidisciplinary approach is providing optimal audibility through sensory devices (HAs and CIs). My experience as a clinical pediatric audiologist motivates me to address key clinical questions with evidence based research.
Evaluation of Revised Indicatons (ERID) for Cochlear Implant Candidacy for the Adult CMS Population
Purpose: The purpose of this study is 1) to evaluate the safety and efficacy of currently available multichannel cochlear implant systems for newly implanted adults with an indication based on open-set sentence recognition that expand criteria currently used by Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), and 2) to assess the correlation between measures of speech recognition in candidates for cochlear implants and their utility in predicting audiologic and quality of life outcomes after implantation.
For more information, contact: Teresa Zwolan, PhD (734-998-8119, zwolan@umich.edu) or Craig Buchman (314-362-7667, buchmanc@wustl.edu)
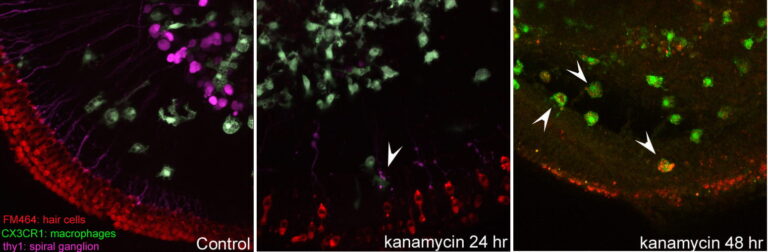
Hirose Lab
After various forms of injury, the inner ear degenerates and inflammatory cells exit the blood vessels and enter the fluid spaces of the cochlea. To what degree these inflammatory cells could be helpful for repair or could serve to exacerbate injury is uncertain. We use methods to image live macrophages in cultures of the mouse inner ear as well as methods to suppress monocytes and macrophages in living mice to determine how these cells affect injury in the cochlea after exposure to ototoxic medications, noise damage or other insults that affect the survival of inner ear sensory cells.
Immunotherapy With MK-3475 in Surgically Resectable Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Brief Summary:
The goal of this trial is to test the ability of MK-3475 (pembrolizumab) to improve locoregional recurrence and distant metastatic rates in high-risk patients with locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCCs) that are treated with current standard of care surgical approaches.
For more information, contact: Douglas R. Adkins, MD, 314-362-4471, dadkins@wustl.edu
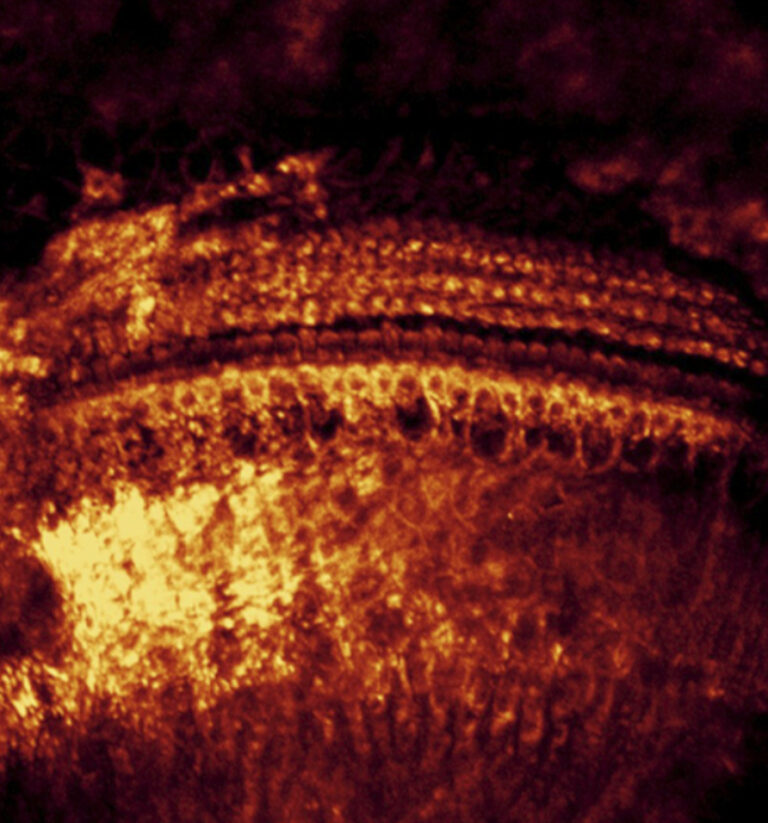
Kim Lab
The ability to obtain multicellular functional images in vivo has transformed neuroscience research, especially the field of sensory physiology. Our novel surgical methods allow real-time visualization of multiple cochlear cells in hearing-preserved animals. We use these approaches to help characterize the properties of sound coding and processing in the cochlea and along the central auditory pathway. Our efforts will also shed light on the transport of ototoxic drugs into the cochlea and promote the development of pathway blockers to prevent drug-induced hearing loss.
Lieu Lab
Our current research focuses on the effects and consequences of hearing loss in children, especially unilateral hearing loss (hearing loss in one ear). We use clinical epidemiology research methods and collaborate with colleagues in neuroscience, psychology, and auditory science to investigate speech-language, cognition, educational effects, executive functioning, and quality-of-life in children with hearing loss. We hope to identify factors that can lead to targeted earlier intervention and possibly better educational performance or language skills acquisition in the future.