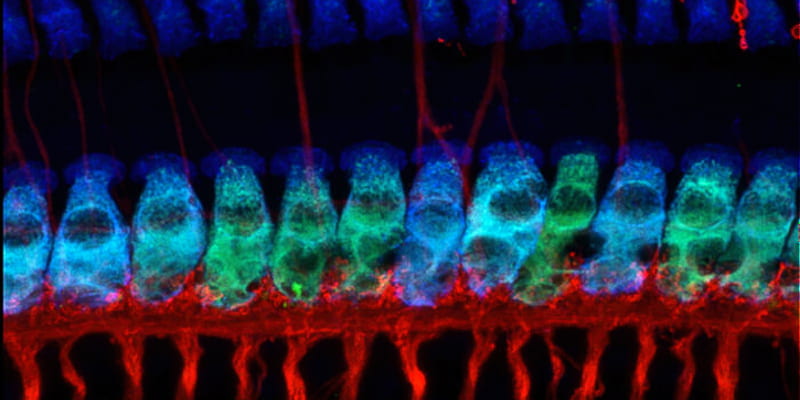
The laboratory of Mark Rutherford, PhD, contributed to studies that show noise-induced hearing loss can be blocked while allowing hearing to continue. The work was published in the Feb. 3, 2020 issue of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). Popular YouTube science news channel SciShow has also reported on the story.
Noise-induced hearing loss blocked with drug compound